Introduction
As organizations move deeper into cloud services, remote work, and online platforms, identity has become the new control plane. Networks no longer define trust. Devices change constantly. Applications interact across environments. What remains consistent is identity. In the digital world, a person's identity is defined by unique attributes — individual pieces of data that distinguish them from others and are used to verify their identity.
In 2026, data identity refers to the unique set of characteristics that distinguish an entity in the digital world. This includes people, devices, applications, and nonhuman entities such as APIs and service accounts. Each of these entities is assigned a unique digital identity, which plays a central role in authentication and authorization processes within IT ecosystems. For IT professionals, understanding data identity is essential to securing access, protecting sensitive data, and maintaining regulatory compliance across distributed systems.
Digital identities are critical for establishing trust in electronic transactions between individuals and organizations. Without reliable identity data, systems cannot determine who should gain access, what permissions apply, or whether activity is legitimate. The core security goals of digital identity systems are Confidentiality, Integrity, and Availability (CIA Triad).
Data Identity
Data identity is the collection of attributes that uniquely represent a person, device, or entity in digital systems. Digital identifiers, such as unique codes or tokens, are essential for distinguishing entities in identity management and authentication. It creates a comprehensive digital profile, encompassing all electronic data related to an entity.
Key Components of Data Identity
Data identity combines various pieces of information that distinguish one entity from another. These include direct identifiers, personalization data, and verification methods. Examples range from usernames and login credentials to device information, behavioral signals, and biometric data. Other data points, such as online activity or hardware attributes, also contribute to verifying and establishing digital identity.
Data identity includes direct identifiers, personalization data, and verification methods. It supports operational efficiency by reducing friction for employees while automating access onboarding and offboarding. For IT teams, this means fewer manual processes and stronger access controls aligned with real business needs.
Digital Identity
A digital identity is a profile or set of information tied to a specific user, machine, or other entity in an IT ecosystem. Digital identities are a collection of data points that comprise the characteristics, attributes, and activities that identify an entity. A person's digital identity is established through a combination of attributes, credentials, and verification methods.
Examples of Digital Identity Data
Digital identities include information such as usernames, email addresses, biometric data, browsing history, and online profiles. They can include both personal data and activity data, such as past orders and device identifiers.
Digital identities are important because they are the basis for authentication and authorization. Username and password combinations remain fundamental components for verifying digital identity in online systems. Digital identities allow a person or device to be recognized and authenticated in the digital world, enabling systems to grant permissions based on identity and role.
With traditional network boundaries dissolved, security in 2026 focuses on identity-first security and zero-trust architectures. Identity is now the primary way systems distinguish between authorized users and unauthorized users.
Identity Verification
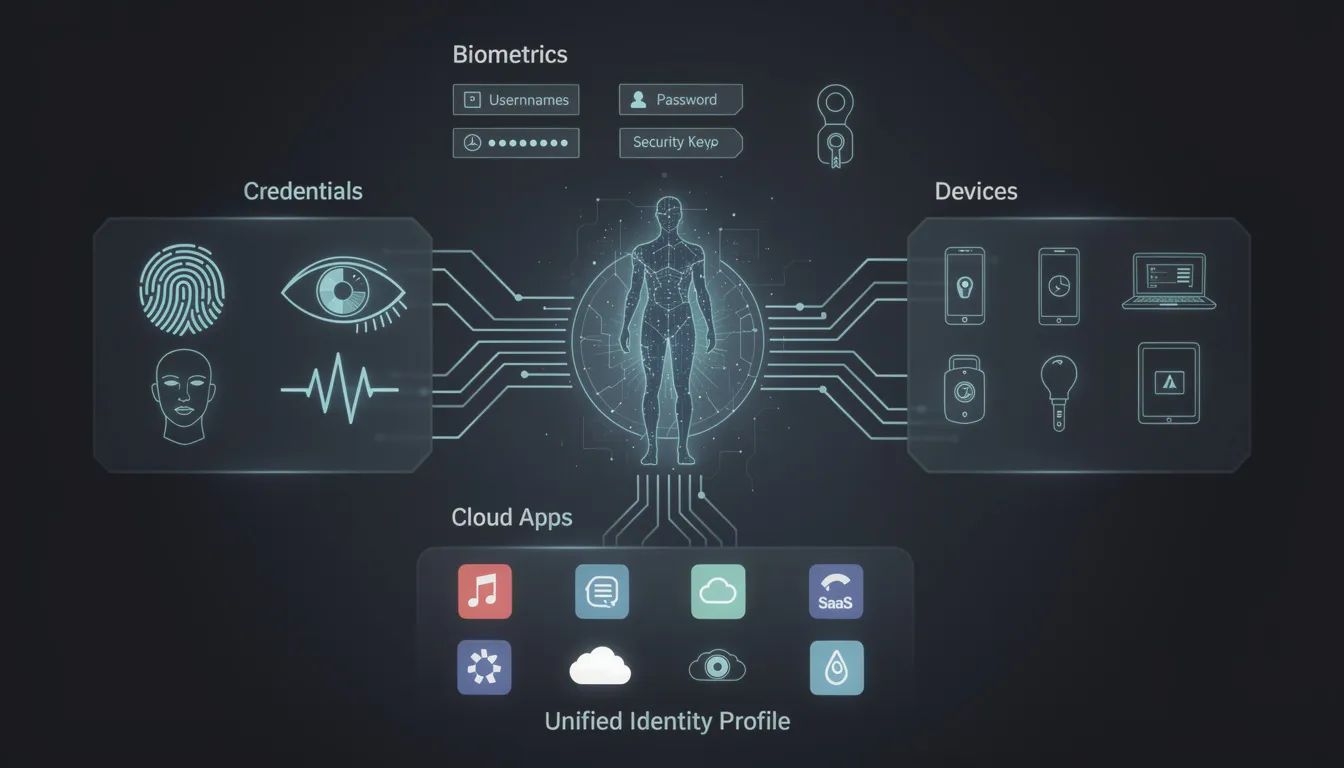
Identity verification is strong authentication to confirm user or device legitimacy. Digital identity verification involves authenticating the presented digital identity against trusted sources through methods like passwords, biometric authentication, and multi-factor authentication.
The ability to establish and verify an individual's digital identity is crucial for preventing fraud and identity theft. Organizations should implement identity verification processes to reduce the risk of fraud and identity theft while improving user experience.
Digital identity verification processes help organizations perform risk-based decision making tailored to individuals. Digital identity verification can streamline authentication processes and improve user experience, especially when paired with modern access management tools.
Digital ID
Digital ID systems often use digital credentials such as a chipped ID card, digital certificate, or mobile-based identity stored on a device. Governments often use digital credentials to streamline and secure the delivery of government services.
Digital identities can be used to verify identity in both the physical and online realms. Digital identity can be used to verify patients and doctors quickly before sending private healthcare data electronically.
As e government services expand, digital ID solutions play a critical role in ensuring that only authorized users can access sensitive systems. In healthcare, digital identity solutions help verify insurance, monitor health devices, and ensure compliance with regulations like HIPAA for secure patient data sharing.
Access Management
Digital identities are critical to identity and access management (IAM) systems that enforce cybersecurity measures and control user access to digital resources. Identity verification and authorization protocols are essential for allowing access to users, applications, and other devices securely, ensuring that only validated digital credentials are used to grant permissions.
Digital identities enable organizations to verify the legitimacy of entities trying to access resources and grant permissions based on identity and role. Data identity enables systems to verify users and grant appropriate permissions using principles like least privilege.
Digital identities simplify access management in enterprise and cloud environments, allowing users to use all the cloud applications they need with one set of strong credentials.
Solutions like EveryKey approach access from a presence-based perspective, using proximity and continuous identity confirmation to make access feel natural while maintaining control. This reinforces the idea that trust should be continuously confirmed, not assumed. Machine digital identities also include other devices, such as IoT nodes and bots, which use unique identifiers for authentication and resource access, in addition to nonhuman entities such as APIs and service accounts.
Data Privacy
Data identity helps meet regulatory requirements by managing and protecting sensitive identity data. Digital identities can help organizations comply with data privacy and sovereignty regulations by ensuring that only authorized users can access certain data sets.
Data minimization involves collecting only necessary data for a specific, lawful purpose. Purpose limitation requires using data only for the reasons it was collected, with user consent. Strong privacy and security measures are a must have for digital identity systems to gain user trust and regulatory approval.
Maintaining privacy requires careful control over identity information such as date of birth, social security number, driver’s license data, and biometric data. Organizations should educate employees about the importance of digital identity protection and best practices.
Data Breaches
The theft of valid accounts is one of the most common ways that cybercriminals break into victim environments, accounting for 30% of all incidents. Data breaches in 2026 are costly, with U.S. averages remaining high due to increased regulatory fines and remediation expenses.
Digital identities help organizations track user activity and distinguish between authorized and unauthorized users. Monitoring online accounts regularly can help detect unauthorized access and protect digital identities.
Using strong passwords and multifactor authentication (MFA) can help protect digital identities from theft and misuse.
Driver’s License and Physical Identity
Digital identities increasingly mirror physical credentials. Driver’s license data, chipped ID cards, and government-issued identifiers are often linked to digital identity systems for identity verification.
Digital identities are established based on a combination of inherent attributes and user-generated data. This allows identity systems to verify individuals across different platforms and devices.
Password Manager
Passwords remain a foundational part of identity systems. Password managers help users maintain strong credentials across online accounts and digital platforms.
Using a password manager supports secure passwords, protects stored passwords, and reduces the risk of credential reuse. Password managers allow users to maintain privacy while simplifying identity verification workflows.
Digital identities are the basis for authentication and authorization, and password managers play a supporting role in protecting identity information.
E Commerce
Digital identities enable sellers to deliver better customer experiences tailored to individual users based on their personal data. Data identity allows businesses to deliver tailored experiences, building customer satisfaction while ensuring interactions with trusted entities.
In e commerce environments, identity verification protects customers, reduces fraud, and ensures secure access to online accounts.
Financial Services
Digital identity management systems help organizations protect sensitive data and financial assets from identity fraud. Digital identities are also used to verify identity for bank account access and secure online banking transactions. Financial services firms rely on digital identity verification to protect bank accounts, manage access, and meet regulatory compliance obligations.
Digital identities help organizations comply with regulations by ensuring that only authorized users can see certain data sets and that access logs are accurate and complete. Digital identities can also streamline the contracting process in B2B transactions by automating the verification of parties involved, including external partners.
Digital identities enable patients to securely share health data with their providers, making it faster and easier to get multiple opinions before determining a medical treatment plan. Similar principles apply across financial and government services.
The Role of Digital Identities in Online Communities
Digital identities are foundational to the way individuals interact, share, and access online services within modern online communities. Each person’s digital identity is made up of a unique combination of digital data points — such as biometric data, login credentials, and device information — that collectively verify their identity and distinguish them from others in the digital world.

In online communities, digital identity verification is essential for maintaining trust, protecting sensitive data, and ensuring that only authorized users can access specific resources. Digital identity systems and solutions are designed to manage user access, control system access, and verify identity, allowing individuals to securely access online services, participate in discussions, and manage their online presence. This is especially important for platforms that handle sensitive information, such as financial services firms, government agencies, and healthcare providers, where regulatory compliance and data privacy are paramount.
Digital credentials, including digital certificates and biometric data, play a key role in authenticating users and authorizing access to sensitive data. By leveraging robust digital identity verification processes — such as multifactor authentication, biometric scans, and secure password management — organizations can prevent identity theft, reduce the risk of data breaches, and ensure that only authorized users gain access to online accounts and cloud resources.
The use of digital identities in online communities also brings important considerations around data privacy and regulatory compliance. Individuals must be aware of how their digital identity data is collected, used, and shared, while organizations are responsible for implementing strong access controls and adhering to regulations such as GDPR, PCI DSS, HIPAA, and GLBA. These measures help protect sensitive data, maintain online privacy, and build trust among users.
Benefits of Digital Identities in Online Communities
Key benefits of digital identities in online communities include:
Enhanced security and trust between users and platforms
Improved data privacy and protection of sensitive information
Streamlined access management and simplified user experience
Increased regulatory compliance for organizations
Reduced risk of identity theft and fraud
Greater control over online presence and digital credentials
Challenges of Managing Digital Identities
However, managing digital identities in online communities also presents challenges:
Ensuring the accuracy and reliability of digital identity data
Preventing unauthorized access and data breaches
Maintaining user trust and confidence in digital platforms
Balancing security requirements with user convenience
Keeping pace with evolving regulatory standards and emerging technologies
To address these challenges, organizations are adopting advanced digital identity verification technologies, such as biometric authentication, digital certificates, multifactor authentication, and AI-powered identity management solutions. Best practices for individuals include using strong, unique passwords, enabling multifactor authentication, monitoring online accounts, and being cautious with personal information shared on digital platforms.
As online communities continue to grow and evolve, the importance of digital identities will only increase. Emerging trends such as decentralized identity systems, blockchain-based verification, and the integration of AI and IoT are shaping the future of digital identity management. By staying informed and proactive, both individuals and organizations can ensure a secure, trusted, and privacy-respecting online environment.
In summary, digital identities are essential for enabling secure access to online services, protecting sensitive data, and fostering trust in online communities. As technology and regulations evolve, ongoing innovation and vigilance will be key to safeguarding digital identities and supporting the continued growth of online interactions.
The Future of Data Identity
Data management in 2026 has evolved into a strategic control plane that governs data access and trust in distributed environments. Digital identities are increasingly important as more services move online, requiring robust verification processes to prevent unauthorized access. Digital identities are now used in a vast array of industries and scenarios, reflecting their broad applicability in both cloud and enterprise environments. For example, digital identities are used in the travel and hospitality, telecommunications, and education sectors to protect online data via identity verification.
Decentralized Identity (DID) utilizes blockchain to allow individuals to provide credential keys without sharing all personal information. Meanwhile, the EU AI Act, effective August 2, 2026, requires strict provenance for training data in AI governance.
Data identity helps close vulnerabilities in the identity layer and strengthen data protections against identity-based attacks.
Conclusion
Data identity is no longer just an IT concept. It is the foundation of trust, access, and privacy in modern digital systems. Digital identities enable organizations to verify legitimacy, manage access, protect sensitive data, and comply with regulations.
For IT professionals, understanding data identity is essential to building secure, scalable systems that support users, devices, and applications across cloud and hybrid environments. When identity is handled well, access becomes seamless, controlled, and human.
FAQ: Data Identity
What is data identity?
Data identity is the collection of attributes that uniquely represent a person, device, or entity in digital systems. It creates a comprehensive digital profile, encompassing all electronic data related to an entity, and combines various pieces of information that distinguish one entity from another, including direct identifiers, personalization data, and verification methods.
How does data identity differ from digital identity?
Data identity refers to the underlying data points, while digital identity is the profile formed from those attributes.
Why is data identity important for security?
Digital identities are the basis for authentication and authorization.
They help prevent unauthorized access.
They reduce the risk of identity theft.
How does data identity support compliance?
Data identity helps meet regulatory requirements by managing access.
It enables logging of activity.
It protects sensitive identity data.
How does EveryKey relate to data identity?
EveryKey focuses on access that is continuously confirmed through presence and proximity, aligning identity with real-world context while maintaining privacy and control.
